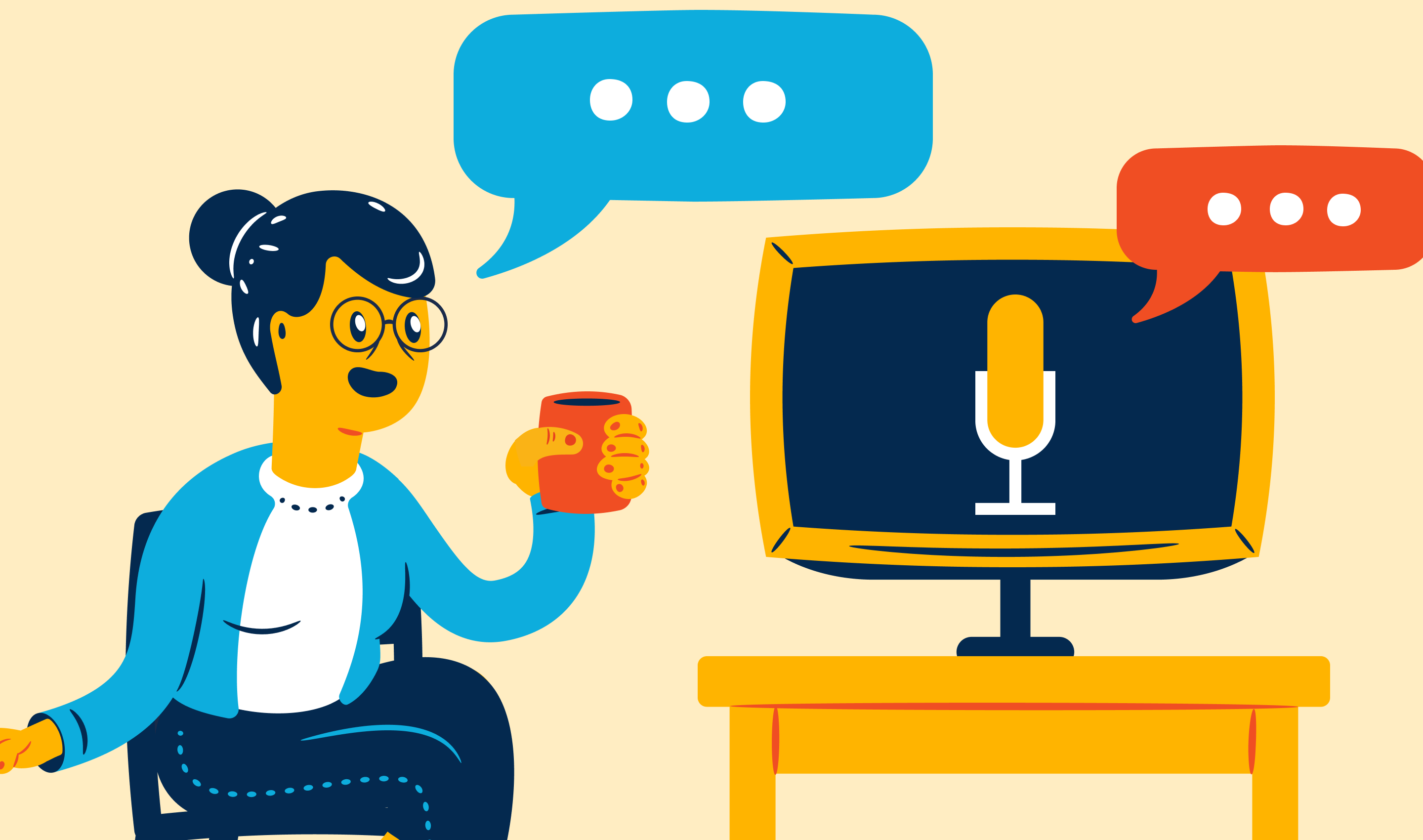
Zero UI: Redefining the Future of Human-Technology Interaction

Zero UI represents a fresh approach to user interface design aimed at reducing reliance on conventional graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Instead, Zero UI enables users to interact with devices and applications using instinctive and natural methods, such as voice commands, gestures, and haptic feedback.
Table of Contents
Changes in User Interfaces Through the Ages
The development of user interfaces has been guided by the goal of establishing more instinctive and user-friendly methods for interacting with technology. Early GUIs were based on the metaphor of a desktop, with windows, icons, and menus. As technology has advanced, GUIs have become more graphical and interactive, with features such as animation, drag-and-drop, and touch-screen input.
Defining Zero UI
Zero UI is a user interface designed with the intention of being inconspicuous and unobtrusive. The goal of Zero UI is to create a user experience that is so seamless and natural that users don’t even realize they are interacting with a device.
Significance of Zero UI for Businesses
Zero UI has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses interact with their customers. Below are several reasons illustrating the significance of Zero UI for businesses.
Increased accessibility: Zero UI can make technology more accessible to people with disabilities. For example, voice-based interfaces can be used by people who are blind or have limited mobility.
Increased efficiency: Zero UI can make it easier for users to complete tasks. As an illustration, gesture-based interfaces enable device control without the need to visually focus on a screen.
Increased personalization: Zero UI can be used to provide users with more personalized experiences. For example, ambient computing can be used to understand the user’s context and provide them with relevant information and services.
Improved customer experience: Zero UI can improve the customer experience by making it easier for users to interact with businesses. For example, voice-based interfaces can be used to provide customer service or to make purchases.
New business opportunities: Zero UI can generate fresh business opportunities by enabling companies to offer innovative products and services. For example, businesses could use Zero UI to create virtual assistants that can help customers with tasks or to create gesture-based interfaces for smart home devices.
Examples of Zero UI in Action
Currently, various real-world examples of Zero UI implementations can be observed. Here are some examples of Zero UI in action:

Amazon Echo: The Amazon Echo is a voice-activated speaker that uses Zero UI to allow users to control devices and applications with their voice. For example, users can ask the Echo to play music, set timers, and control smart home devices.
Google Home: The Google Home is another voice-activated speaker that uses Zero UI. Similar to the Amazon Echo, users can ask the Google Home to do things like play music, set timers, and control smart home devices.
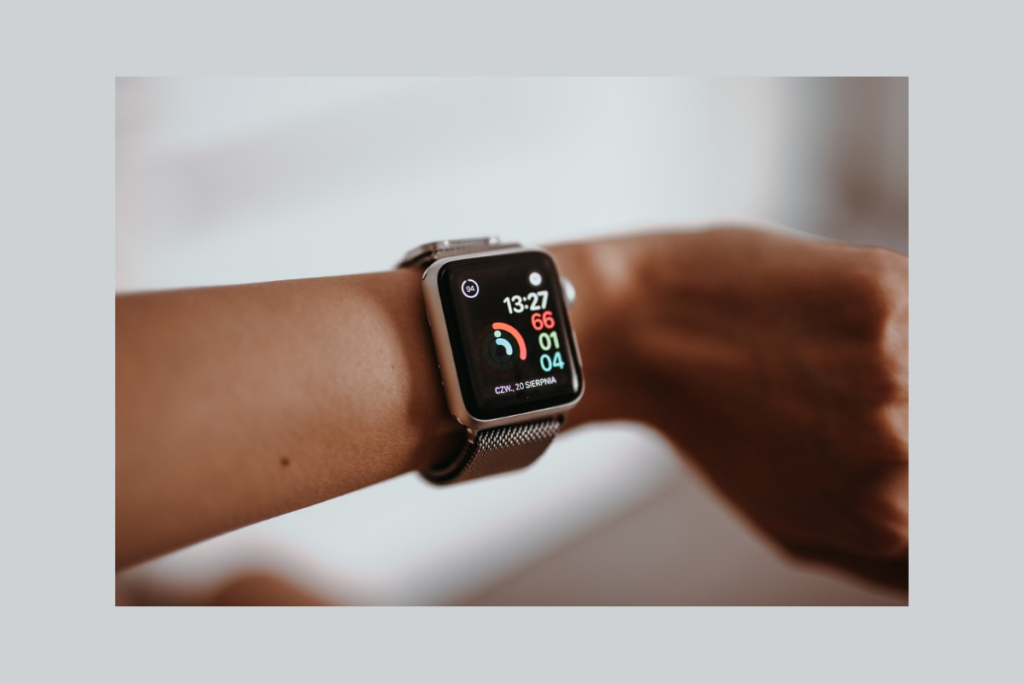

Apple Watch: The Apple Watch uses a combination of voice commands and gesture recognition to allow users to interact with the device. For example, users can use voice commands to send messages, make calls, and control music playback. They can also use gestures to scroll through notifications, dismiss alarms, and activate Apple Pay.
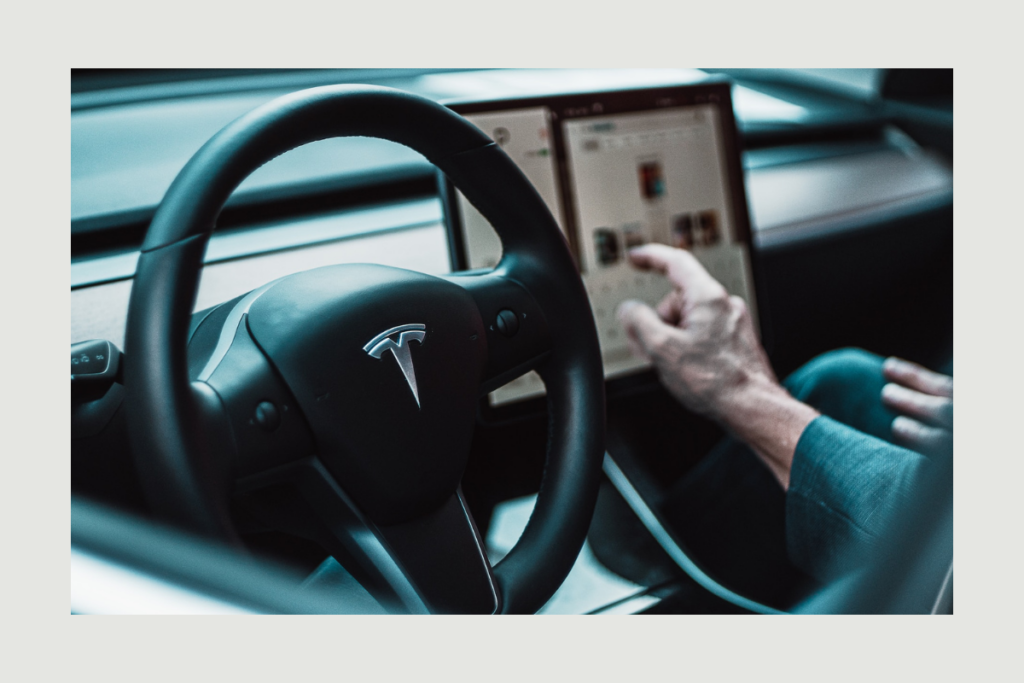

Tesla cars: Tesla cars use a variety of Zero UI technologies, including voice commands, gesture recognition, and facial recognition. For example, drivers can use voice commands to control the car’s climate control system, navigation system, and entertainment system. They can also use gesture recognition to control the car’s media player and answer phone calls.
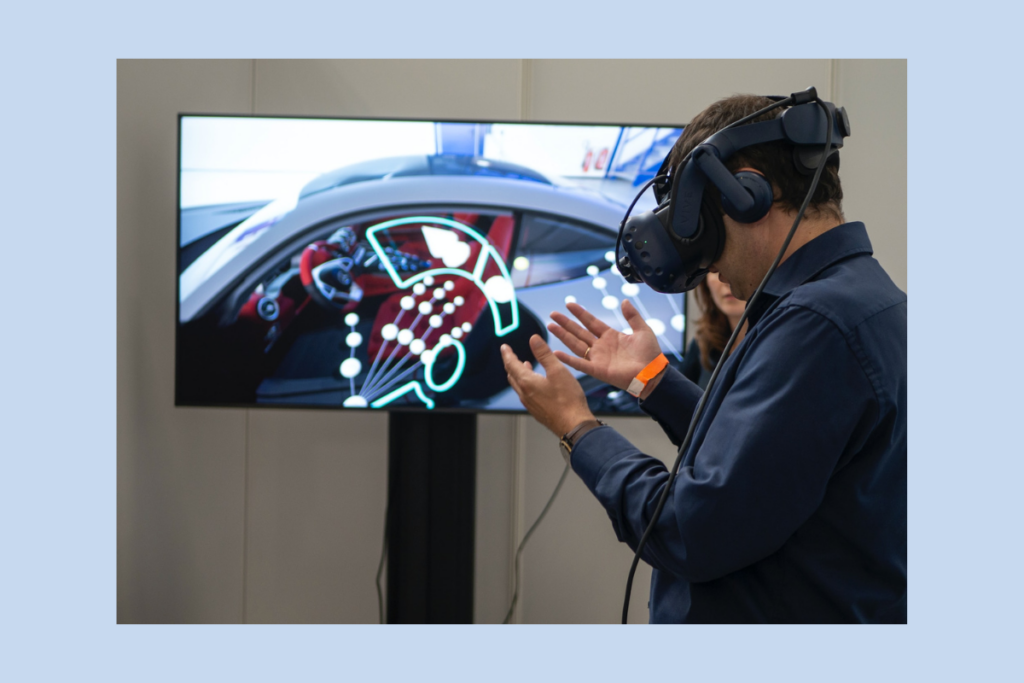

Microsoft HoloLens: The Microsoft HoloLens is a mixed reality headset that uses Zero UI to allow users to interact with virtual objects. As an instance, users can utilize gestures to manipulate virtual objects, and they can employ voice commands to engage with virtual assistants.
Key Components and Technologies
There are a number of key components and technologies that are essential to Zero UI. These include:
Voice recognition and natural language processing: These are transformative technologies that enable users to engage with devices and applications using their voice as input.
Gesture recognition: This technology empowers users to engage with devices and applications using gestures like swiping, tapping, and pinching.
Haptic feedback: This technology provides users with physical feedback, such as vibrations, to help them interact with devices and applications.
Ambient computing and contextual awareness: These technologies allow devices and applications to understand the user’s context, such as their location, activity, and preferences.
This information can be used to provide users with more personalized and relevant experiences.
These technologies play a vital role in Zero UI as they enable users to interact with devices and applications in a manner that is natural and intuitive. For example, voice recognition allows users to interact with devices without having to look at a screen, and gesture recognition allows users to interact with devices without having to touch them. Haptic feedback can further enrich the user experience by delivering physical sensations, such as vibrations, when users interact with devices.
Ambient computing and contextual awareness play a crucial role in Zero UI as they enable devices and applications to comprehend the user’s context.This information can be used to provide users with more personalized and relevant experiences. For example, if a user is in a car, a device could understand the user’s context and provide them with information about traffic or directions.
These are just some of the key components and technologies that are essential to Zero UI. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative ways to interact with devices and applications in a natural and intuitive way.
Growing Popularity of Voice Assistants
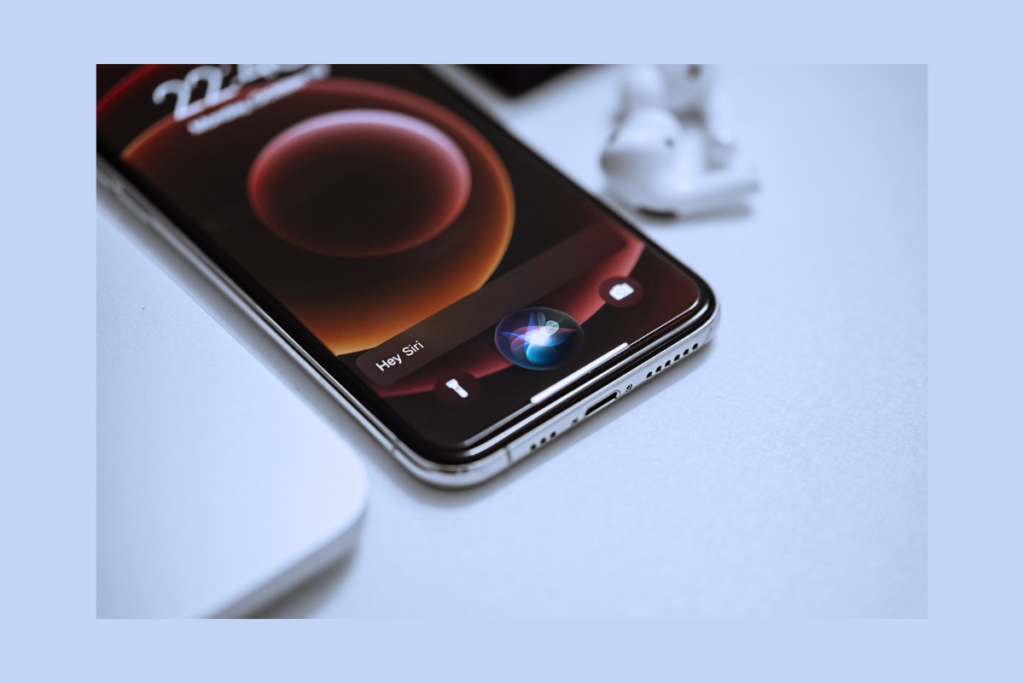

In recent years, voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri have experienced a surge in popularity. These virtual assistants empower users to effortlessly interact with devices and applications using voice commands, significantly simplifying the process of accessing and utilizing technology.
Natural Language Processing and Understanding
The increasing popularity of voice assistants has driven advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and understanding (NLU). NLP refers to computers’ ability to comprehend human language, while NLU involves their capability to interpret the meaning behind human language. These advancements have resulted in voice assistants becoming capable of understanding more intricate and nuanced voice commands.
Conversational Design Principles
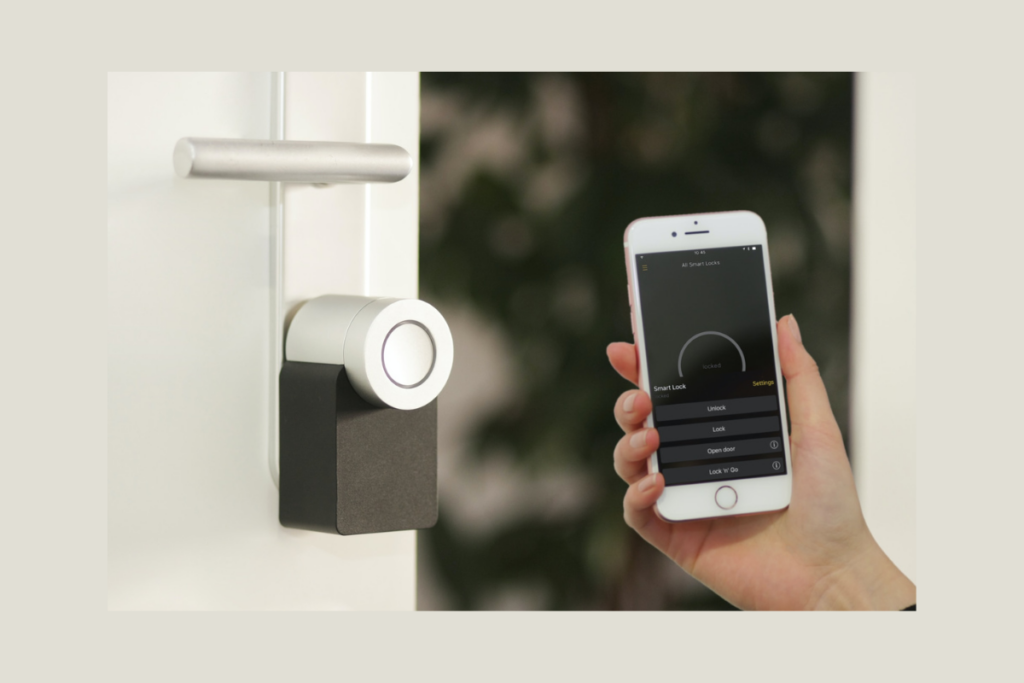

Conversational design is a set of principles that can be used to create effective voice-based interfaces. These principles include:
Use natural language: Voice assistants should use natural language that is easy for users to understand. This means using simple, conversational language that is similar to how people speak to each other.
Be consistent: Voice assistants should use consistent terminology and commands. This means using the same words and phrases to refer to the same thing. This will help users learn how to interact with the voice assistant and avoid confusion.
Be clear and concise: Voice assistants should be clear and concise in their instructions. This means using short, simple sentences that are easy to understand. It is also important to avoid using jargon or technical terms that users may not understand.
Be informative: Voice assistants should provide users with information about their requests. This means providing users with feedback on what the voice assistant is doing and why. It is also important to provide users with information about the results of their requests.
Be helpful: Voice assistants should be helpful and provide users with assistance when needed. This means being able to answer user questions and resolve user problems. It is also important to be able to adapt to user needs and preferences.
Here are some additional tips for designing effective voice-based interfaces:
Use simple, direct commands: Users should be able to give voice commands in a natural way. Avoid using complex commands or jargon.
Be aware of the user’s context: The user’s context, such as their location, activity, and preferences, should be taken into account when designing voice commands.
Provide feedback: Users should be provided with feedback on their voice commands. This will help them learn how to interact with the voice assistant and avoid frustration.
Be error-tolerant: Voice assistants should be able to handle errors gracefully. This means being able to understand user commands even if they are not perfect.
Gesture and Motion-based Interfaces
Gesture Recognition Technology
Gesture recognition technology enables users to engage with devices and applications using gestures like swiping, tapping, and pinching. Its growing popularity stems from the fact that it provides a more natural and intuitive means of interaction with devices, fostering a seamless user experience.
Motion Sensors and Cameras
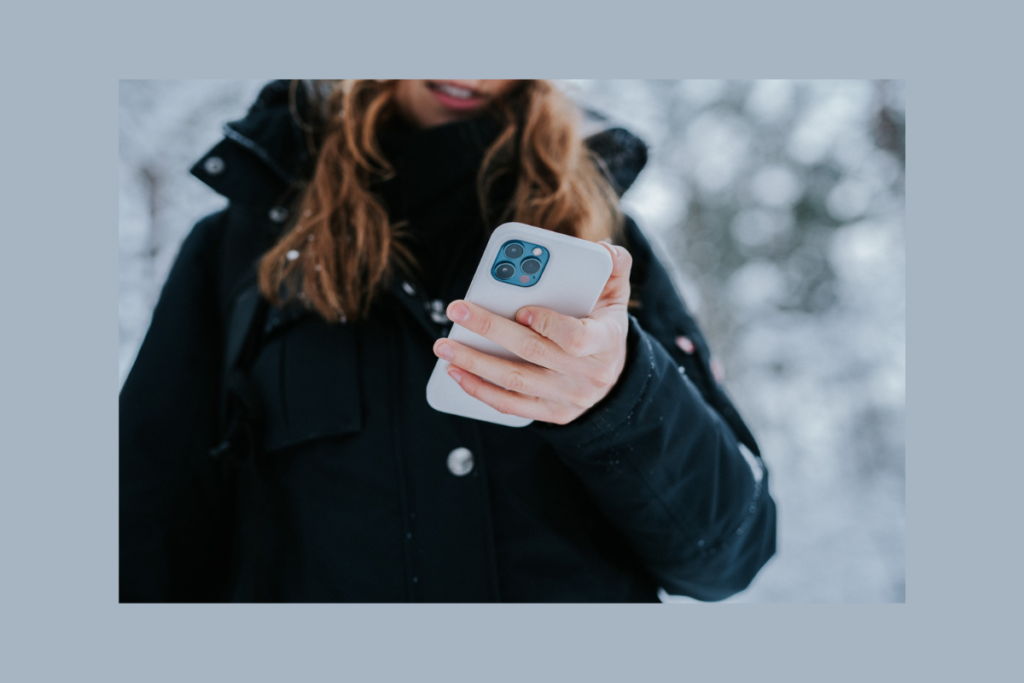

Motion sensors and cameras can also be used to create gesture-based interfaces. For example, the iPhone X uses facial recognition to unlock the device and authorize payments. And the Microsoft HoloLens uses motion sensors and cameras to track the user’s head and hand movements, allowing users to interact with holograms in a natural way.
Designing for Gesture-based Interactions
When designing for gesture-based interactions, it is important to consider the following factors:
The user’s context: The user’s context, such as their location, activity, and preferences, should be taken into account when designing gesture-based interactions. For example, a gesture that is appropriate for a user in a car may not be appropriate for a user in a meeting.
The user’s experience: The user’s experience with gesture-based interactions should also be considered. If the user is new to gesture-based interactions, it is important to use simple and intuitive gestures.
The device’s capabilities: The device’s capabilities should also be considered when designing gesture-based interactions. For example, a device with a limited number of sensors may not be able to support complex gestures.
The gesture’s affordance: The affordance of a gesture is the way in which it suggests its function. For example, a swipe gesture typically suggests that the user is trying to scroll through a list. When designing gesture-based interactions, it is important to make sure that the gestures’ affordances are clear and easy to understand.
The gesture’s visibility: The visibility of a gesture is how easy it is for the user to see and perform the gesture. For example, a gesture that is performed in the air is less visible than a gesture that is performed on a touchscreen. When designing gesture-based interactions, it is important to make sure that the gestures are visible and easy to perform.
The gesture’s feedback: The feedback of a gesture is the information that the user receives about the success or failure of the gesture. For example, a haptic feedback or sound can be used to provide feedback to the user. When designing gesture-based interactions, it is important to make sure that the gestures provide clear and informative feedback to the user.
What Is Haptic Technology?
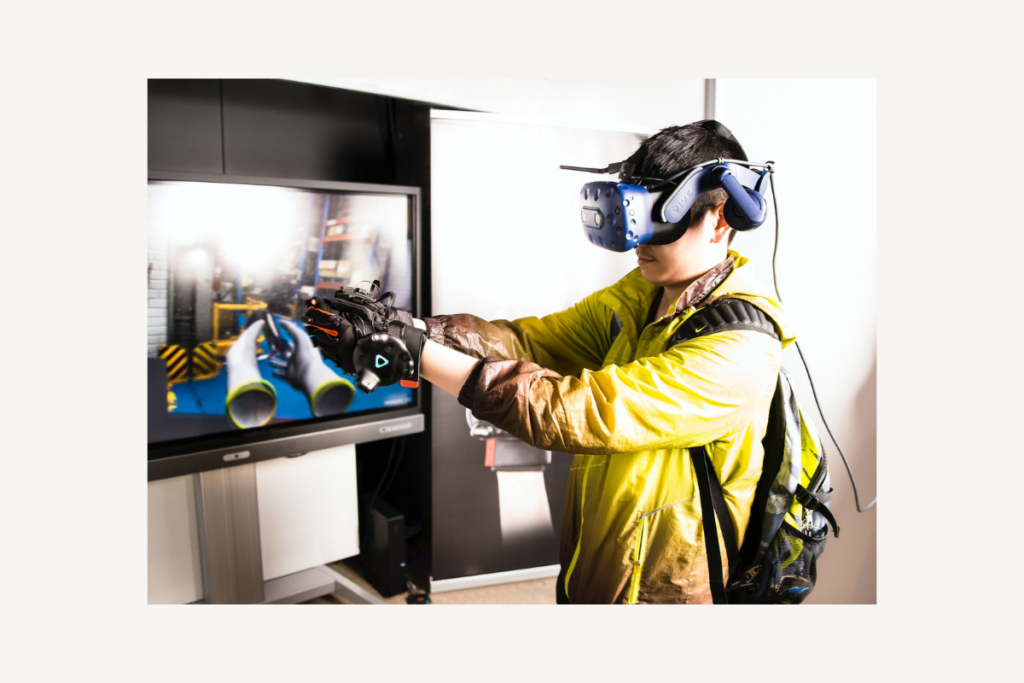

Haptic technology is a technology that delivers physical feedback, like vibrations, to aid users in their interaction with devices and applications. Haptic feedback can be used to enhance the user experience in a number of ways, such as providing feedback on button presses, providing feedback on the movement of objects, and providing feedback on the user’s environment.
Tactile Feedback in Wearable Devices
Haptic feedback is becoming increasingly popular in wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers. These devices use haptic feedback to provide users with information about their activity, such as the number of steps they have taken or the distance they have traveled.
Enhancing User Experience through Touch
Haptic feedback can also be used to enhance the user experience in other devices, such as smartphones and tablets. For example, haptic feedback can be used to provide users with feedback on button presses, providing users with a more tactile and satisfying experience.
Ambient Computing and Contextual Awareness
Contextual Understanding in Smart Environments
Ambient computing is a type of computing that is designed to be invisible to the user. With ambient computing, devices and applications are able to understand the user’s context, such as their location, activity, and preferences. This information can be used to provide users with more personalized and relevant experiences.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network comprising internet-connected physical objects. Through the IoT, devices and applications can communicate with each other, exchanging information seamlessly. This information can be used to provide users with more personalized and relevant experiences.
Anticipatory User Experiences
Ambient computing and the IoT can be used to create anticipatory user experiences. With anticipatory user experiences, devices and applications are able to anticipate the user’s needs and provide them with the information and services they need before they even ask for it.
Implications for Businesses
Zero UI has a number of implications for businesses. These include:
Redefining User Engagement and Interaction
Zero UI has the potential to revolutionize user-business interactions by eliminating the reliance on intricate graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Through this approach, accessing and utilizing products and services becomes simpler and more efficient for users. As a result, businesses may experience heightened levels of engagement, loyalty, and customer satisfaction,.
Opportunities for Personalization and Customization
Zero UI opens up fresh possibilities for businesses to achieve personalization and customization. By comprehending the user’s context, companies can deliver tailored and pertinent experiences to their users. This heightened level of personalization can potentially drive up sales and boost profits for the businesses implementing such strategies.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
Zero UI also presents a number of challenges and considerations for businesses. These include the need for advanced technology, the need for a deep understanding of the user’s context, and the need to design for a variety of devices and platforms.
Below are several concrete examples showcasing how businesses can leverage Zero UI:
Customer service
Zero UI can be used to create more efficient and effective customer service experiences. For example, a customer could use voice commands to interact with a virtual assistant to resolve an issue.
Sales and marketing
Zero UI can be used to create more personalized and relevant sales and marketing campaigns. For example, a business could use ambient computing to understand the user’s context and deliver targeted messages.
Product development
Zero UI can be used to gather feedback from users and improve products and services. For example, a business could use gesture recognition to track user interactions with a product and identify areas for improvement.
Overall, Zero UI has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses interact with their customers. By embracing Zero UI, businesses can create more personalized, relevant, and efficient experiences for their customers.
Industries Embracing Zero UI
A number of industries are already embracing Zero UI. These include:
Automotive: Zero UI is being used in cars and other vehicles to provide drivers with a more hands-free and intuitive driving experience. For example, voice commands can be used to control the radio, navigation system, and climate control.
Smart Home and IoT Devices: Zero UI finds application in smart home devices and various IoT devices, enabling users to control their appliances and gadgets using voice commands or gestures. For example, users can use voice commands to turn on lights, lock doors, and adjust thermostats.
Healthcare and Wellness Applications: Zero UI is being used in healthcare and wellness applications to provide users with a more personalized and engaging experience. For example, users can use voice commands to track their fitness data, manage their medications, and schedule appointments.
Retail: Zero UI is being used in retail stores to provide customers with a more convenient and efficient shopping experience. For example, customers can use voice commands to ask for product information, make purchases, and find their way around the store.
Education: Zero UI is being used in education to provide students with a more interactive and engaging learning experience. For example, students can use voice commands to access educational content, ask questions, and collaborate with classmates.
The Future of Zero UI
Below are some significant trends that are expected to influence the future of Zero UI:
Advances in technology: As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated Zero UI technologies emerge. For example, we can expect to see more advanced voice recognition and gesture recognition technologies, as well as new technologies such as brain-computer interfaces.
Increased personalization and customization: Zero UI has the potential to provide users with more personalized and customized experiences. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see more businesses adopt Zero UI to create more personalized and relevant experiences for their customers.
Integration with other technologies: Zero UI is likely to be integrated with other technologies, such as augmented reality and virtual reality. This will create new and innovative ways for users to interact with devices and applications.
Ethical and privacy concerns: As Zero UI becomes more widespread, there will be a need to address ethical and privacy concerns. For example, there is a need to ensure that users’ personal data is protected and that Zero UI technologies are not used to discriminate against or exploit users.
Overall, the future of Zero UI is bright. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see Zero UI become more widespread and integrated with other technologies. This will create new and innovative ways for users to interact with devices and applications.
Here are some specific examples of how Zero UI might be used in the future:
Virtual assistants: Voice assistants will undergo advancements, becoming more sophisticated and adept at comprehending and responding to natural language commands. For example, users will be able to ask their virtual assistants to do things like book appointments, order food, and control smart home devices.
Gesture-based interfaces: Gesture-based interfaces will become more common and will be used to control devices and applications in a more natural way. For example, users will be able to use gestures to scroll through documents, control music playback, and interact with virtual reality environments.
Ambient computing: Ambient computing will become more widespread and will be used to create more personalized and relevant experiences. For example, users will be able to receive information and notifications based on their location, activity, and preferences.
Zero UI is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. As technology continues to advance, Zero UI is likely to become more popular and widespread.
Conclusion
Zero UI is a new paradigm in user interface design that has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. As technology continues to advance, Zero UI is likely to become more popular and widespread.
Here are some of the benefits of Zero UI:
Increased accessibility: Zero UI can make technology more accessible to people with disabilities. For example, voice-based interfaces can be used by people who are blind or have limited mobility.
Increased efficiency: Zero UI can make it easier for users to complete tasks. For example, gesture-based interfaces can be used to control devices without having to look at a screen.
Increased personalization: Zero UI can be used to provide users with more personalized experiences. For example, ambient computing can be used to understand the user’s context and provide them with relevant information and services.
However, there are also some challenges associated with Zero UI:
Technology requirements: Zero UI requires advanced technology, such as voice recognition and gesture recognition. This technology can be expensive and not all devices have it.
User understanding: Zero UI requires users to understand how to interact with devices and applications in a natural way. This may take some time for users to learn.
Design challenges: Crafting Zero UI interfaces poses significant challenges for designers. They must take into account a diverse range of factors, including the user’s context, the capabilities of the device, and the user’s past experiences with similar interfaces.
In the realm of user interface design, Zero UI stands as a promising and innovative paradigm. Its potential lies in rendering technology more accessible, efficient, and personalized. Nonetheless, there are still hurdles that must be overcome before Zero UI can fully integrate into mainstream usage.
Take your company to the next level and get results with our world class user experience, interface design and implementation.
Get a FREE 30 min Strategy Session

Related posts
Flo’s Empathetic Design Hacks: Crafting Data-Driven Experiences for Female Health Apps
Flo reigns supreme in the realm of female health apps. Boasting over 350 million users, it’s become the go-to resource […]
A Quick Guide to Mobile-First Design
So, why mobile? 🤷♀️ Well, because mobile is now everything – with over 55% of web traffic coming from mobile […]
First Impressions Matter: Crafting Compelling User Onboarding Experiences
User onboarding has become more crucial than ever in today’s fiercely competitive digital landscape, where countless applications and platforms vie […]
Creative product design that gets results
Take your company to the next level with world class user experience and interface design.
get a free strategy session